Byzantine contributed to art through its religous art and architecture They used icons to evoke the presence of God Byzantine contributed to learning because of their preservation of classic works of Ancient Greece They also produced their own history books Byzantine sculpture in the early days The Byzantine sculpture In the early days is more an extensions of the Hellenistic art, were portraits of great impacting aesthetics drama were produced Sculpture underwent changes very similar to those in architecture;Byzantine Paintings Under the Byzantine Empire from the 4th century to the 15th century, painting flourished in many different forms and mediums Most notable form of Byzantine paintings was icon painting which was frequently used as decoration for church interiors as well as simply standalone paintings

Artists In Late Byzantine Period The Workshop Of Michael Astrapas And Eutychios
Byzantine empire art and music
Byzantine empire art and music- On Byzantine Art & Symbolism 1245 pm Published by Gallery Byzantium Sumptuous and rich in color and detail, the art of the Byzantine has transcended the centuries and continues to inspire today At Gallery Byzantium, our pieces are inspired by the art, jewelry, and architecture of this historic empireDeputy director, Courtauld Inst of Art) only partially meets the challenge of making his subject understandable




Byzantine Empire World History Encyclopedia
It's The Byzantine Empire!Shop for byzantine empire wall art from the world's greatest living artists All byzantine empire artwork ships within 48 hours and includes a 30day moneyback guarantee Choose your favorite byzantine empire designs and purchase them as wall art,Summary of Byzantine Art and Architecture Existing for over a thousand years, the Byzantine Empire cultivated diverse and sumptuous arts to engage the viewers' senses and transport them to a more spiritual plane as well as to emphasize the divine rights of the emperor
Thus, Byzantine art includes work created from the fourth century to the fifteenth century and encompassing parts of the Italian peninsula, the eastern edge of the Slavic world, the Middle East, and North Africa So what is Byzantine art, and what do we mean when we use this term?Using bright stones, gold mosaics, lively wall paintings, intricately carved ivory, and precious metals in general, Byzantine artists beautified everything from buildings to books, and their greatest and most lasting legacy is undoubtedly the icons which continue to decorate Christian churches around the worldBecause Byzantine art portrays a society in change, defining the period and its contributions is a big undertaking The author of several books on iconography and Byzantine art, Cormack (history of art, Univ of London;
What kind of art did the Byzantine Empire have?The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople Was used by the Palaiologoi dinasty, a byzantine greek family that is last dinasty of Emperors and Autocrats ofByzantine Empire 8,1 likes 98 talking about this Remembering the art and the culture of the Byzantine Empire (330 1453 AD), its predecessors and its legacy
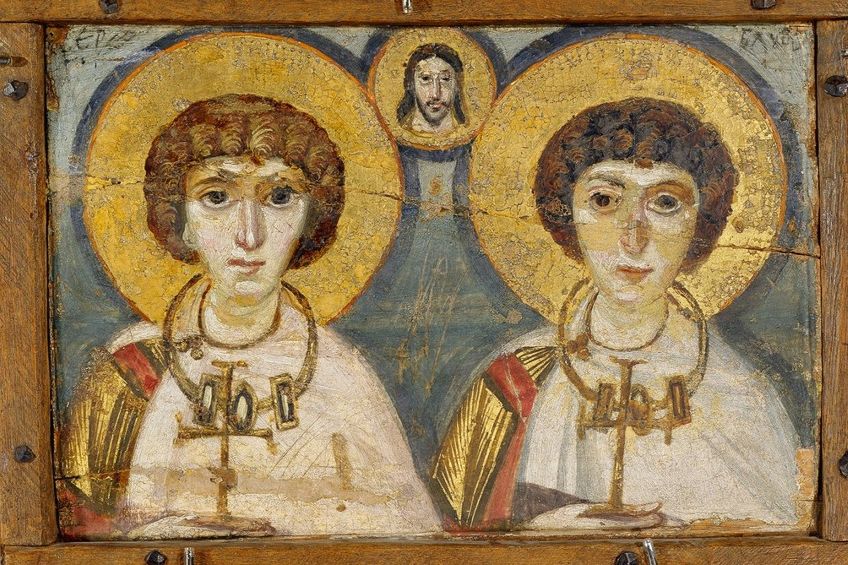




Byzantine Art Traversing The Byzantine Empire Art Period




Art History 8 Byzantine Art Timeline Pink Area To The Right Is Byzantine Ppt Download
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was ConstantinopleIt survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until itByzantine art is the name for the artistic products of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empireOld Roman Empire World Map, 1626 by John Speed Rare Wall Art of Western and Byzantine Framed or Unframed Gift Chart OldmapsShop 5 out of 5 stars (319)



Byzantine Art Wikipedia




The Art Of Gambargin Pelekyphoroi Amazones Of ma Tōn Varangōn Basileia Tōn Rhōmaiōn Hws Medieval Varangian Byzantine Empire Women Warriors Concept Historically Wrong Sketch Series Historical Commentary For An Empire
Art and architecture flourished during the Middle Byzantine period, owing to the empire's growing wealth and broad base of affluent patrons Manuscript production reached an apogee ( ), as did works in cloisonné enamel ( ;Byzantine art, the visual arts and architecture produced during the Middle Ages in the Byzantine Empire Almost entirely concerned with religious expression, Byzantine art is known for the mosaics covering the interior of domed churches They often feature flat and frontal figures floating on a golden backgroundContent from both Christianity and classical Greek mythology were artistically expressed through Hellenistic modes of style and iconography




A Dreamy Journey Through Byzantine Mosaics Mozaico Blog



1
This momentous event inspired much of the art of the following four centuries, which comprises the second great era of Byzantine culture and provides the starting point of this volume The Glory of Byzantium , and the exhibition that it accompanies, concludes with the demise of the empire's role as a world power, evidenced by the LatinAbout Art produced in the Byzantine empire (or Eastern Roman Empire)—at its height, a territory that spanned large swaths of the Mediterranean, presentday Turkey, Southern Spain, and Italy—between the 4th and 15th centuries, when it fell to the Ottoman TurksExplore Sarah Torres's board "Justinian and Theodora" on See more ideas about byzantine empire, byzantine, byzantine art




Empress Theodora Byzantine Empire Basilica Of San Vitale Byzantine Art World Mosaic Textile Byzantine Art Png Pngegg
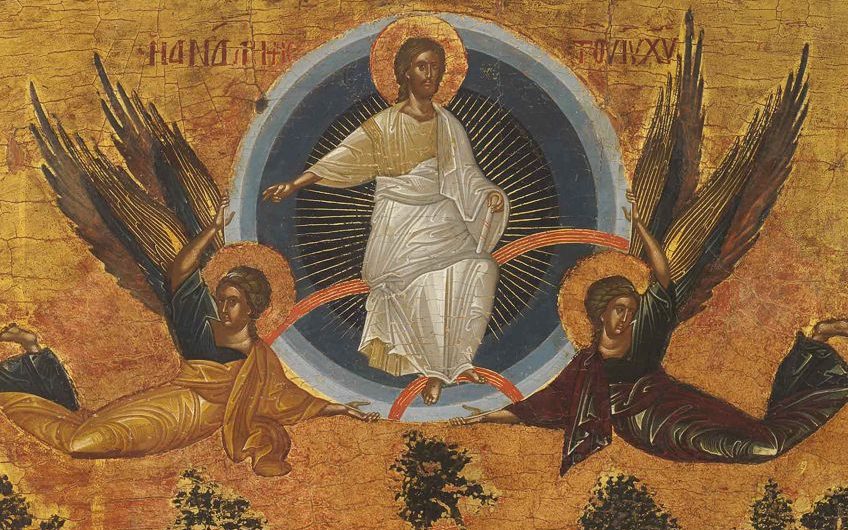




Byzantine Art Traversing The Byzantine Empire Art Period
Fun facts about the Byzantine Empire Byzantine art is almost entirely focused on religion The official language of the Byzantine Empire was Latin until 700 CE when it was changed to Greek by Emperor Heraclius Constantinople was attacked and plundered byUnique Byzantine Empire Posters designed and sold by artists Shop affordable wall art to hang in dorms, bedrooms, offices, or anywhere blank walls aren't welcomeThe Byzantine Empire was influenced by the Hellenistic culture created by the conquests of Alexander the Great Learning and trade thrived in the Byzantine Empire As you read in a previous chapter, Emperor Constantine ended the persecution of Christians, and Emperor Theodosius made Christianity the official state religion of the Roman Empire




Byzantine Empire Etsy




170 Byzantium Ideas Byzantine Empire Eastern Roman Roman Empire
Byzantine art comprises the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome and lasted until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the start date of the Byzantine period is rather clearer in art history than in political history, if still imprecise Unlike Roman art, Byzantine art appears to the modern viewer to have made few attempts to mimic reality Images are often twodimensional and flat, and is antinaturalistic in its most basic form Art in the Byzantine Empire was largely dedicated to religious and imperial purposes, and decorated the interior of churches most prominently The Byzantine Empire continued to exist for another thousand years until it would later fall to the Ottoman Turkish Empire in 1453 Throughout its history, the Byzantine Empire achieved a high level of art and culture that would have an impact on the civilizations that followed Traces of Byzantine art can still be found in the artwork of the



Art In Italy Byzantine Art Podere Santa Pia Holiday House In The South Of Tuscany



Jesus Art Iii Jesus In History And Culture
Surviving Byzantine art is mostly religious and, for the most part, highly conventionalized, following traditional models that translate their carefully controlled church theology into artistic terms Painting in frescos, mosaics, and illuminated manuscripts, and on wood panels were the main, twodimensional mediaByzantine art began after the Edict of Milan by Roman Emperor Constantine and lasted until the Ottomans (turkish) Empire captured Constantinople Most, if not all artworks in Byzantine art was religious based Byzantine art glorified Christianity and express its mystery Mosaic artworks were very popular during the Byzantine eraThe Deesis Mosaic, Hagia Sophia, Istanbul In Byzantine art, and later Eastern Orthodox art generally, the Deësis or Deisis (Greek δέησις, "prayer" or "supplication"), is a traditional iconic representation of Christ in Majesty or Christ Pantocrator enthroned, carrying a book, and flanked by the Virgin Mary and St John the Baptist, and sometimes other saints and angels




Byzantine Art World History Encyclopedia




The Byzantine Empire Charles W C Oman Westholme Publishing
Although not as famous as the Italian or Northern Renaissance, Byzantine art was a significant period in the history of Western art Known for its extravagant mosaics and dazzling use of gold, this style is deeply intertwined with the rise of Christianity in Europe, with many murals still decorating churches throughout the MediterraneanChoose your favorite byzantine empire paintings from 74 available designs All byzantine empire paintings ship within 48 hours and include a 30day moneyback guaranteeLate Byzantine (c 1261–1453) was a twilight time for the Byzantine empire, after the invasion of European crusaders damaged trade and infrastructure Byzantine art was the dominant visual language in Europe for much of the Middle Ages , due to the Byzantine Empire's centuries in power, and the massive wealth and industry accumulated in




Ppt Byzantine Art Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




10 Most Famous Byzantine Artworks Artist Poplab
Byzantine Empire Art First Christian emperor Was known for founding the 'new rome' which brought back the idea f christianity In which ways did the Byzantine Empire adhere to and project the idea of a New Rome?In which ways was it a continuation of the Roman Empire?Review of Keys Works of Early Byzantine ArtOverview of Early Byzantine Period Overview of Byzantine Empire and Constantinople Overview of




Artstation Byzantine And Georgian Empire Concept Art Akaki Makatsaria
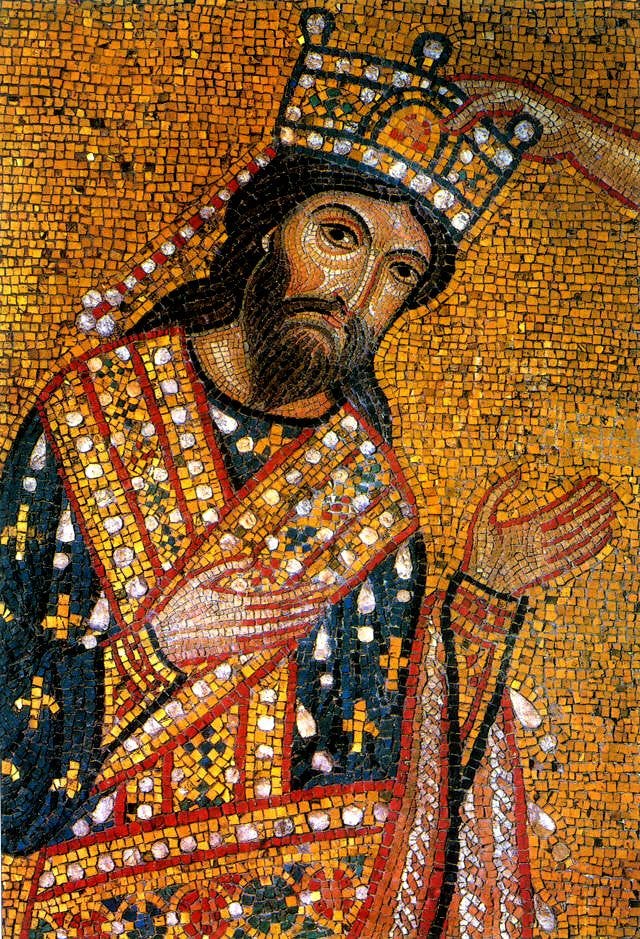




Roman Empire Byzantine Art The Byzantine Empire Also Referred To By Exposition Art Blog Medium
Arts of the Ancient Mediterranean and Byzantium Portrait Bust of a Woman, Mid–2nd century AD Rome The Art Institute's Arts of the Ancient Mediterranean and Byzantium department showcases the origins and early development of Western art from the dawn of the third millennium BCE to the time of the great Byzantine EmpireHeaven and Earth Art of Byzantium from Greek Collections is the first exhibition devoted to Byzantine art at the Gallery It presents life in Byzantium through approximately 170 works of art dating from the inception of the empire to its close Byzantine art originated and evolved from the Christianized Greek culture of the Eastern Roman Empire;
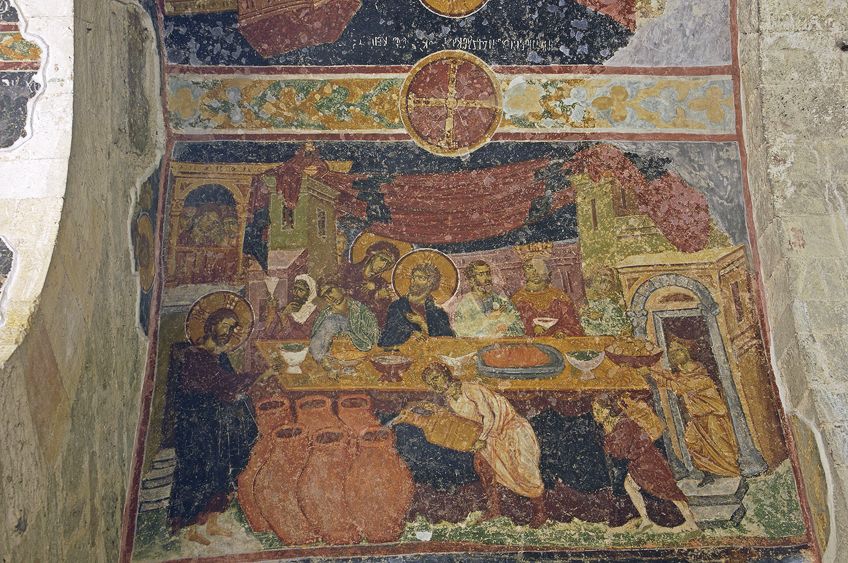




Byzantine Art Traversing The Byzantine Empire Art Period




Artists By Art Movement Byzantine Art Wikiart Org
How did the Byzantine Empire contribute to art and education?All the best Byzantine Empire Painting 33 collected on this page Feel free to explore, study and enjoy paintings with PaintingValleycomWere several good examples of secular architecture survive from that period
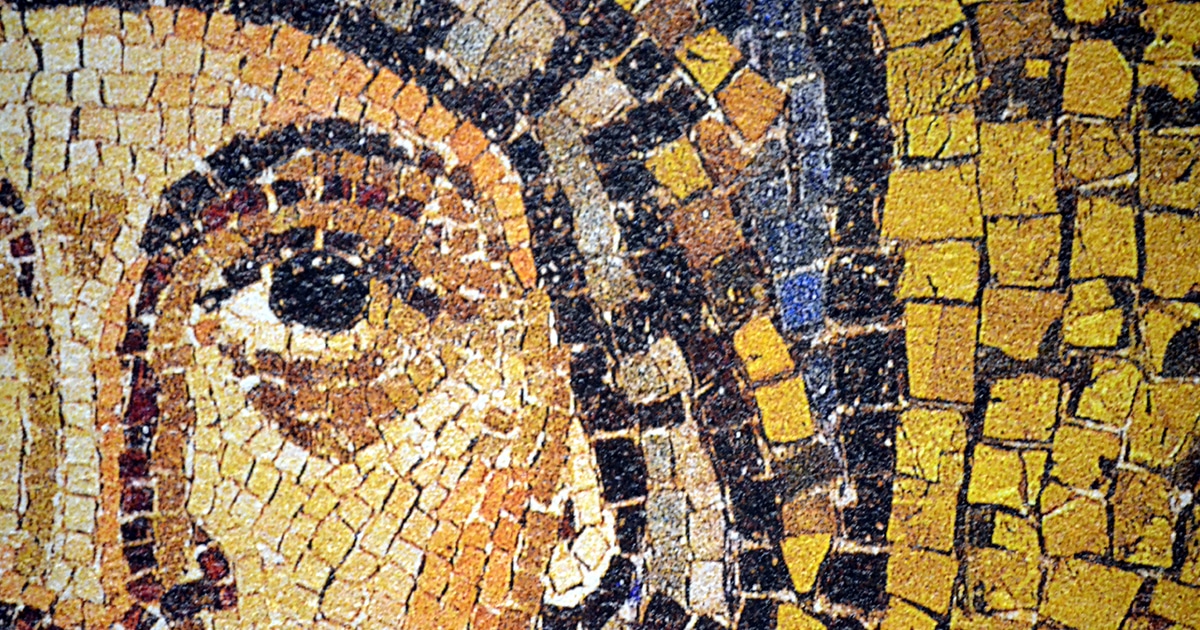




Learn About The History And Characteristics Of Byzantine Art




5 105 Byzantine Art Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
Byzantine art The Roman Empire continued as the Byzantine Empire, with its capital at Constantinople c 330 1453 CEMosaics were one of the most popular forms of art in the Byzantine Empire They were extensively used to depict religious subjects on the interior of churches within the Empire and remained a popular form of expression from 6th century to the end of the Empire in the 15th centuryCheck out how late Imperial Rome transformed in the centuries from Constantine to Justinian, as it evol




Byzantine Empire World History Encyclopedia



History Of Art Spring Summer 11 Courses




Unit 1 The Art Of The Byzantine Empire




Byzantine Frescoes Ars Artistic Adventure Of Mankind




Early Byzantine Art Boundless Art History




Byzantine Art Wikipedia




A History Of Graphic Design Chapter 9 The Byzantine Art



The Armenian Contribution To The History Of The Byzantine Empire Art A Tsolum




10 Things You May Not Know About The Byzantine Empire History



Q Tbn And9gcskqs2pxmifk1yqychakm2lxzqqfh Jopvxqk Ktbm0me9ewmsm Usqp Cau




Byzantine Art Png Images Pngwing




Roman Empire Byzantine Art The Byzantine Empire Also Referred To By Exposition Art Blog Medium




Rome In The East Art And Architecture Of The Byzantine Empire Brewminate
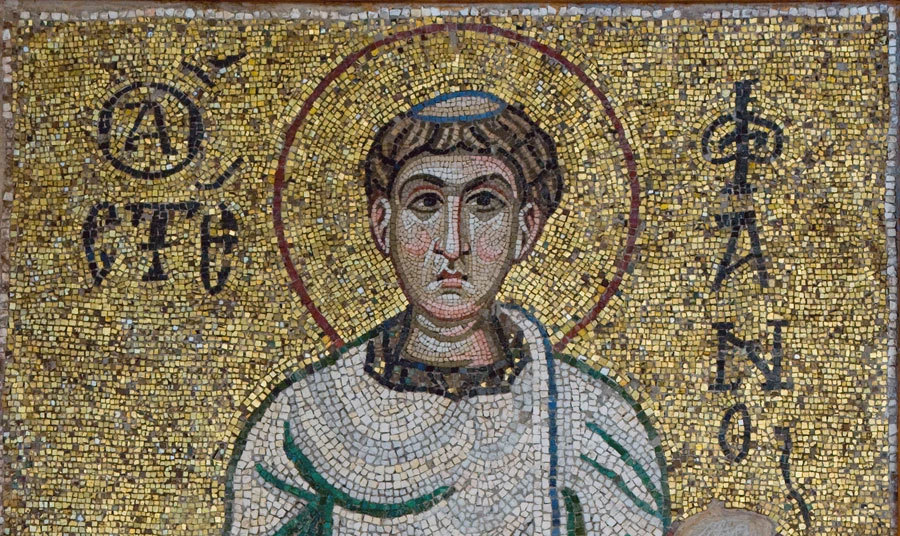




Byzantium 330 1453 Exhibition Royal Academy Of Arts



Byzantine Empire Art And Architecture Architectural Design And Construction Of The Best Buildings




Middle Byzantine Art Smarthistory




Explore The Best Byzantium Art Deviantart



Byzantine Empire Art Characteristics



1




Byzantine Art Wikipedia




The Art Architecture Of The Byzantine Empire Kindle Edition By Ward Kennon Arts Photography Kindle Ebooks Amazon Com




Byzantine Art 8eikes Ekdromes Sta Metewra




A Dash Of Art History Large Museo Nacional De Bellas Artes The Two




The Art Of The Early Byzantine Empire 7 9 10




Byzantine Art Smarthistory



Byzantine Art Characteristics History Facts Britannica




Byzantine Icons The Who What When And Where




Byzantine Empire Picture Of Penticton Art Gallery Tripadvisor




Artists In Late Byzantine Period The Workshop Of Michael Astrapas And Eutychios




List Of 10 Finest Surviving Examples Of Byzantine Art




Mosaics Of The Byzantine Empire My Quest Blog




The Artistic Legacy Of Byzantium Smithsonian Associates




Byzantine Art




Byzantine Art Mosaics History Characteristics Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Did The Byzantine Empire Have The Best Christian Art Quora



Byzantine Art Movement The Arts In New York City
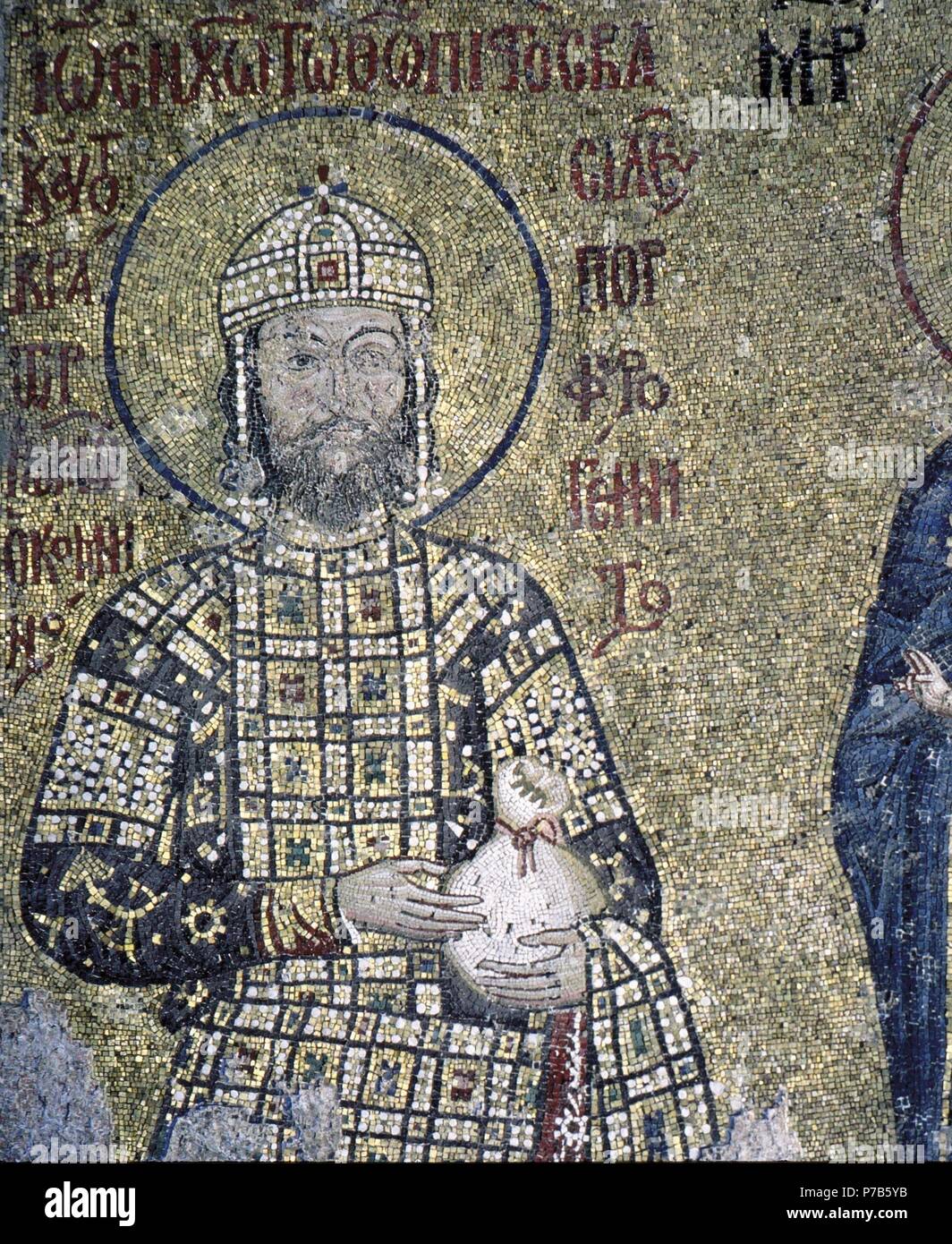




Mosaic Of Emperor John Ii Commenus Ruled Byzantine Empire 1118 43 Haghia Sofia Istanbul Artwork Also Known As Sanctuary Museum Haghia Sofia Stock Photo Alamy



Byzantine Art Four Fs And A G The



A Brief History Of Byzantine Art And Its Characteristics




Empress Theodora Byzantine Empire Mosaic Art Canvas Material Painting Art Mosaic Png Pngwing
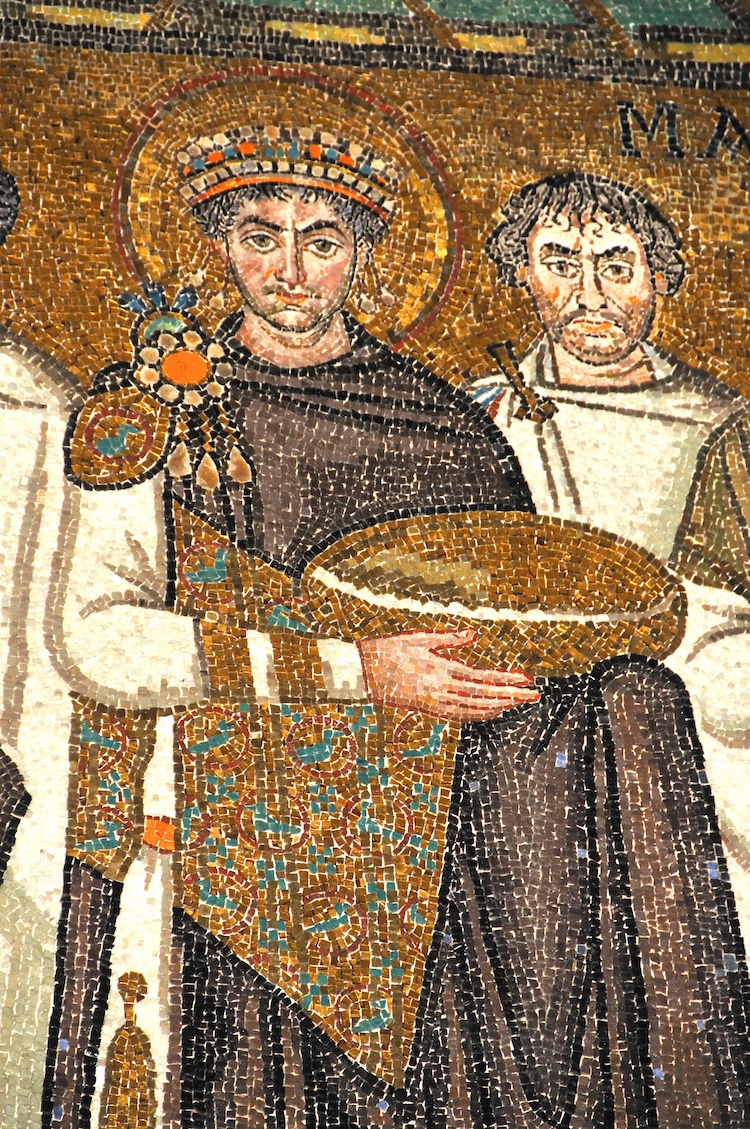




Learn About The History And Characteristics Of Byzantine Art




The Divine Art Of Austerity And Piety In The Byzantine Empire 330 1453 Ad



The Divine Art Of Austerity And Piety In The Byzantine Empire 330 1453 Ad
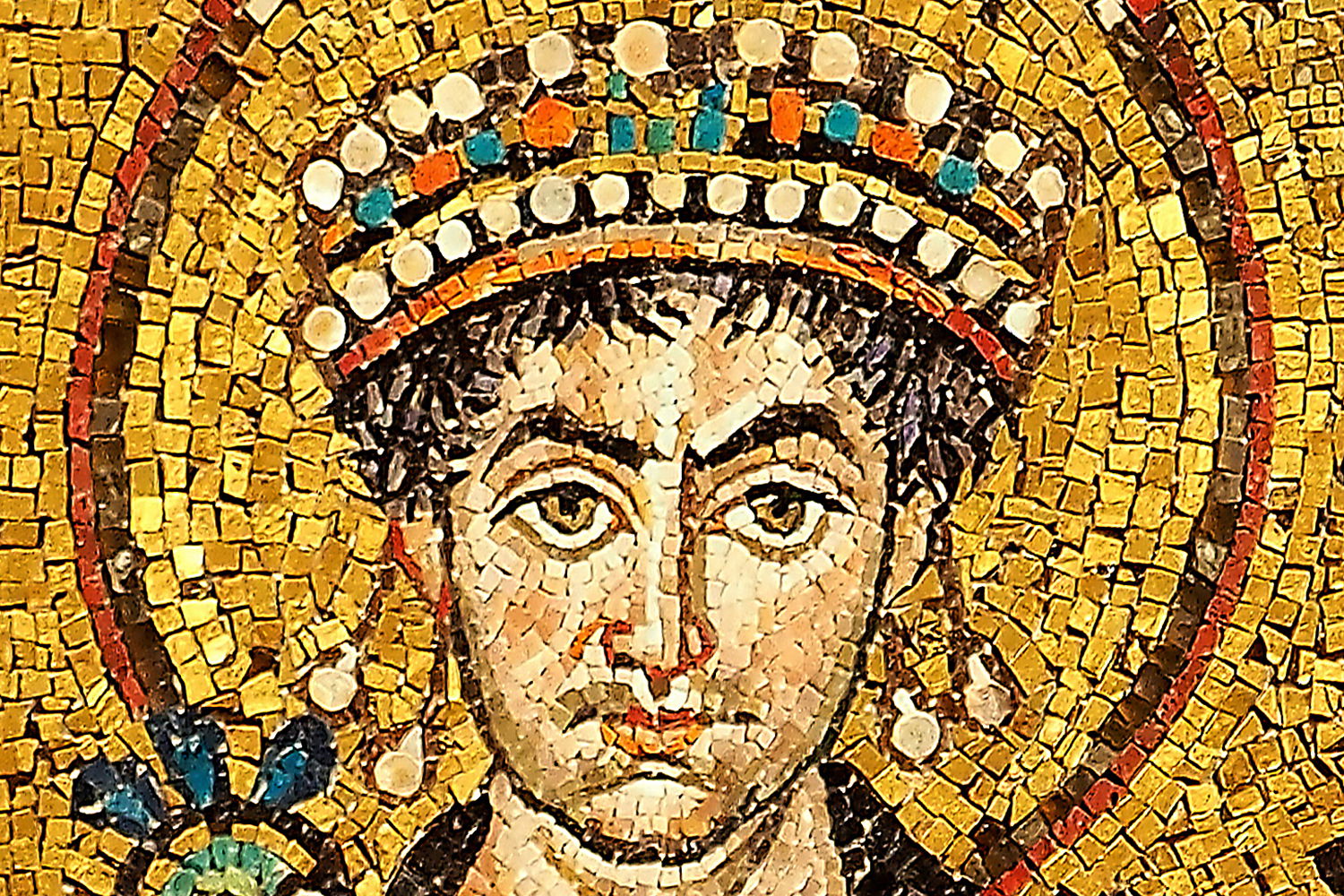




The Elusive Byzantine Empire History Today




Byzantine Art Characteristics History Facts Britannica




10 Interesting Facts About The Byzantine Empire Listverse Byzantine Mosaic Byzantine Art Byzantine Empire



Byzantine Empire Byzantine Art Theotokos Icon Png 591x650px Byzantine Empire Art Byzantine Art Eastern Orthodox Church




Byzantine Empire Wall Art Pixels




Strangest Things The Peculiar Byzantine Empire Quiz Oupblog




Byzantine Archaeology And Art
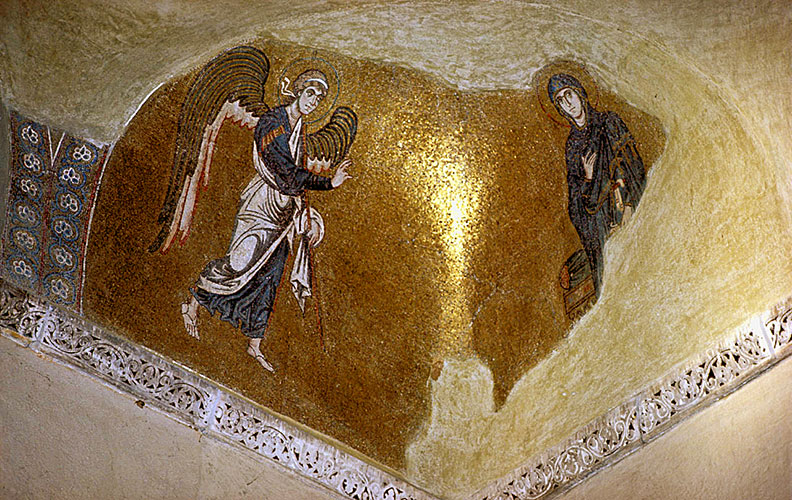




Light Surface Spirit Phenomenology And Aesthetics In Byzantine Art Dumbarton Oaks




Byzantine Empire Wall Art Fine Art America



Byzantine Art




Byzantine Art Artsy



Byzantium Ca 330 1453 Essay The Metropolitan Museum Of Art Heilbrunn Timeline Of Art History




Byzantine Art




Society In The Byzantine Empire World History Encyclopedia



Art In Italy Byzantine Art Podere Santa Pia Holiday House In The South Of Tuscany
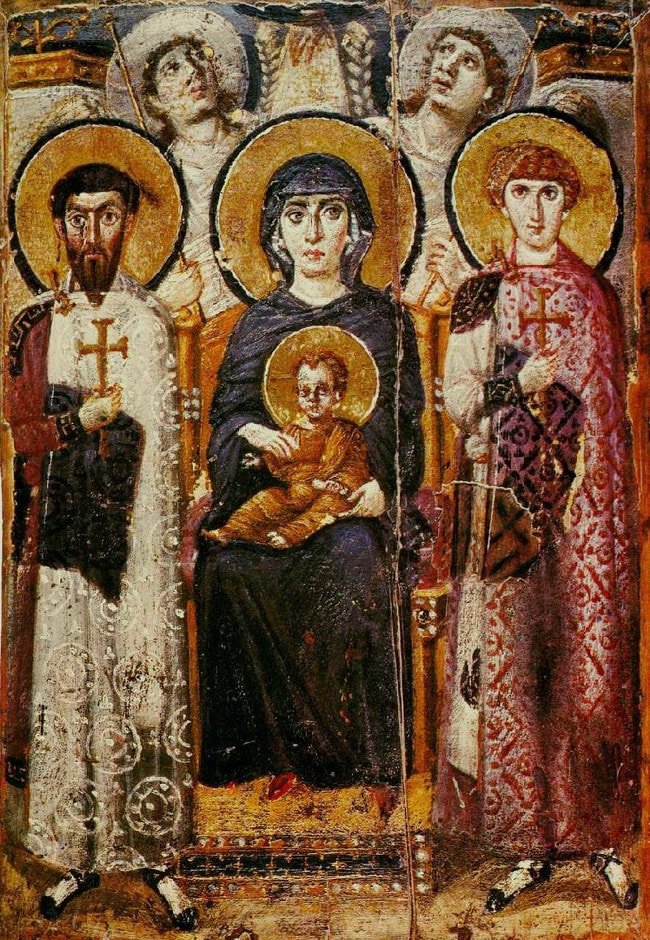




List Of 10 Finest Surviving Examples Of Byzantine Art




Byzantine Art An Introduction Smarthistory



Jesus In Byzantine Art Images Of Jesus




Constantinople And The Byzantine Millennium 330 1453 February 28 March 1 14 Humanities West




16 The Art Of The Early Byzantine Empire Filson Art History 19
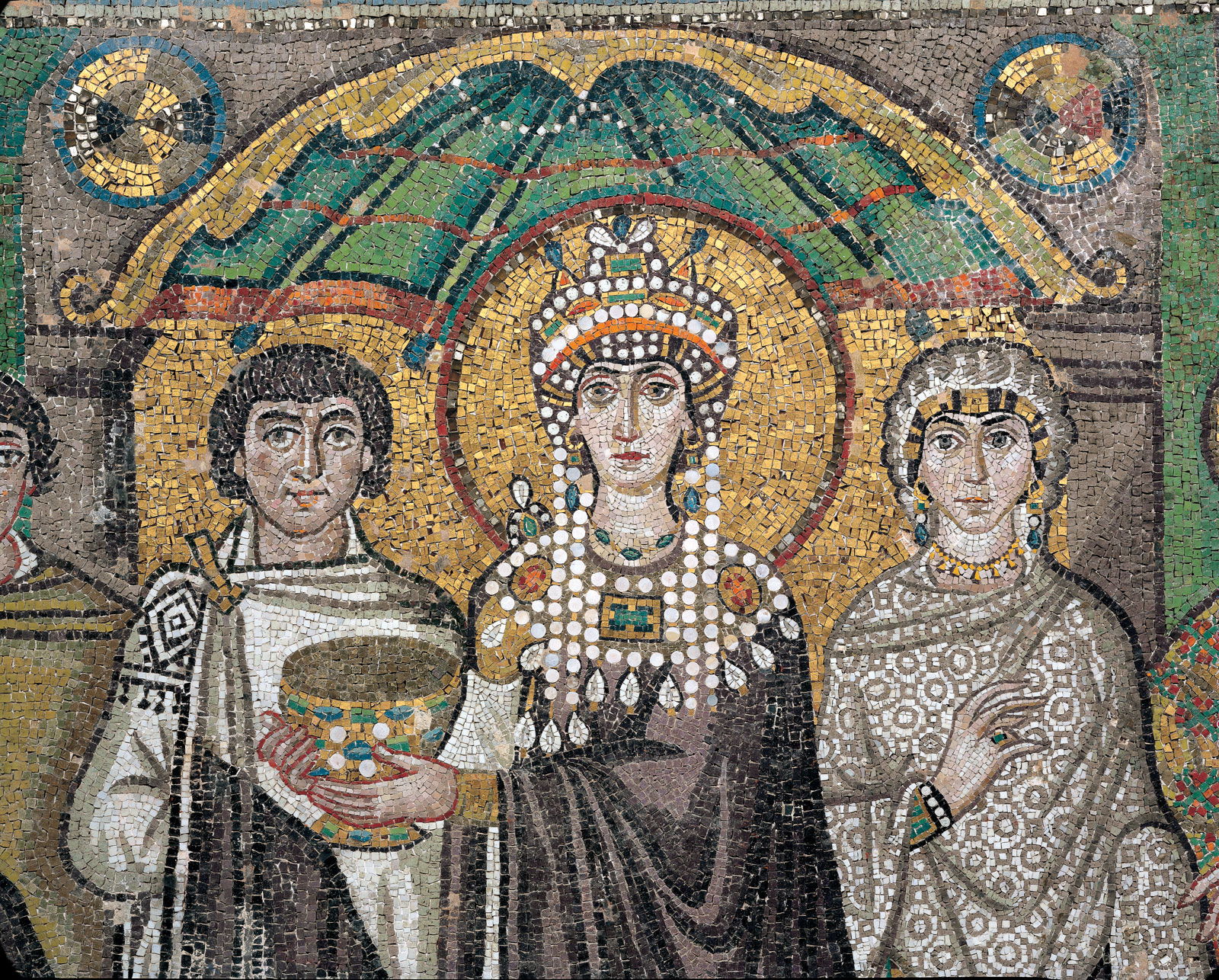




Class Syllabus



Byzantine Painting Art History Summary Periods And Movements Through Time
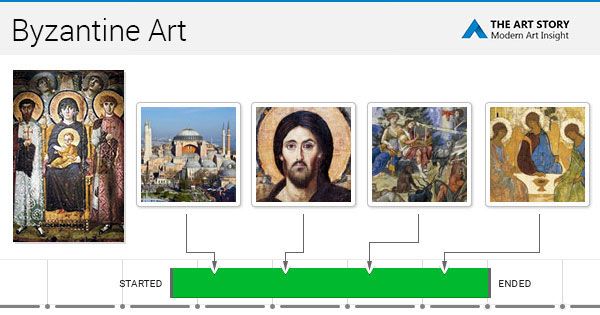



Byzantine Art And Architecture History Theartstory
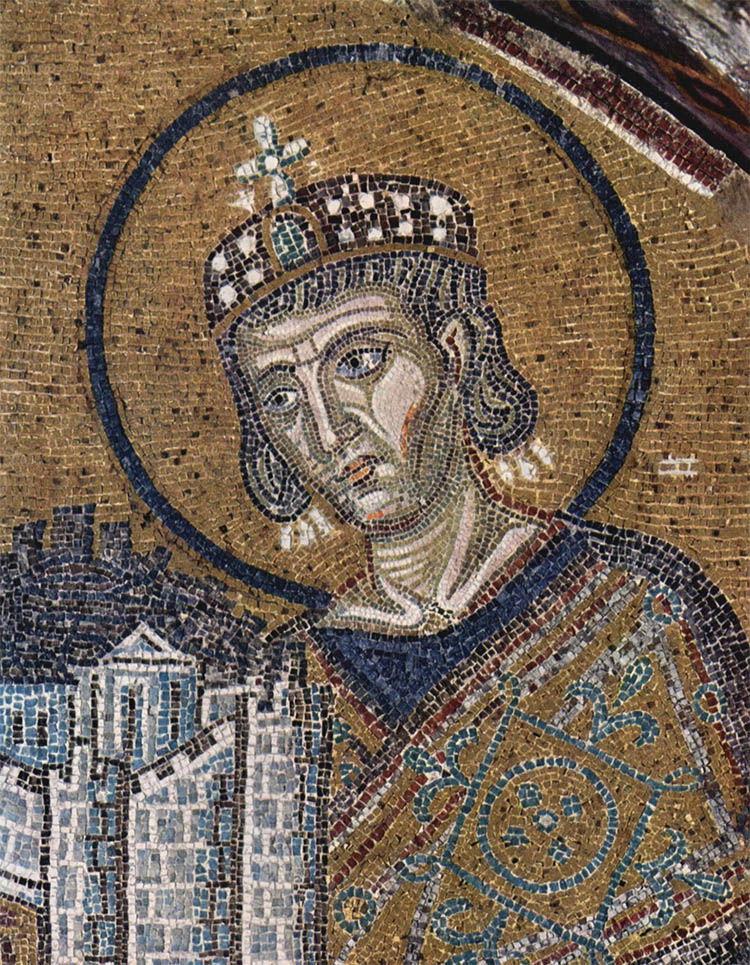




The Elusive Byzantine Empire History Today



Andre Grabar The Art Of The Byzantine Empire Byzantine Art In The Middle Ages Andre Grabar Free Download Borrow And Streaming Internet Archive




Art Of The Byzantine Era World Of Art Rice David Talbot Amazon Com Books




Byzantine Art And Architecture History Theartstory




Byzantine Culture And Society Article Khan Academy




Women In The Byzantine Empire Byzantine Art Byzantine Mosaic Byzantine Empire




Late Antique And Byzantine Art



Q Tbn And9gcrkbyzmtapixi7aoa0n0mleeensr7fuqzagnppd33h4kez9il03 Usqp Cau




Byzantine Empire Wall Art Fine Art America
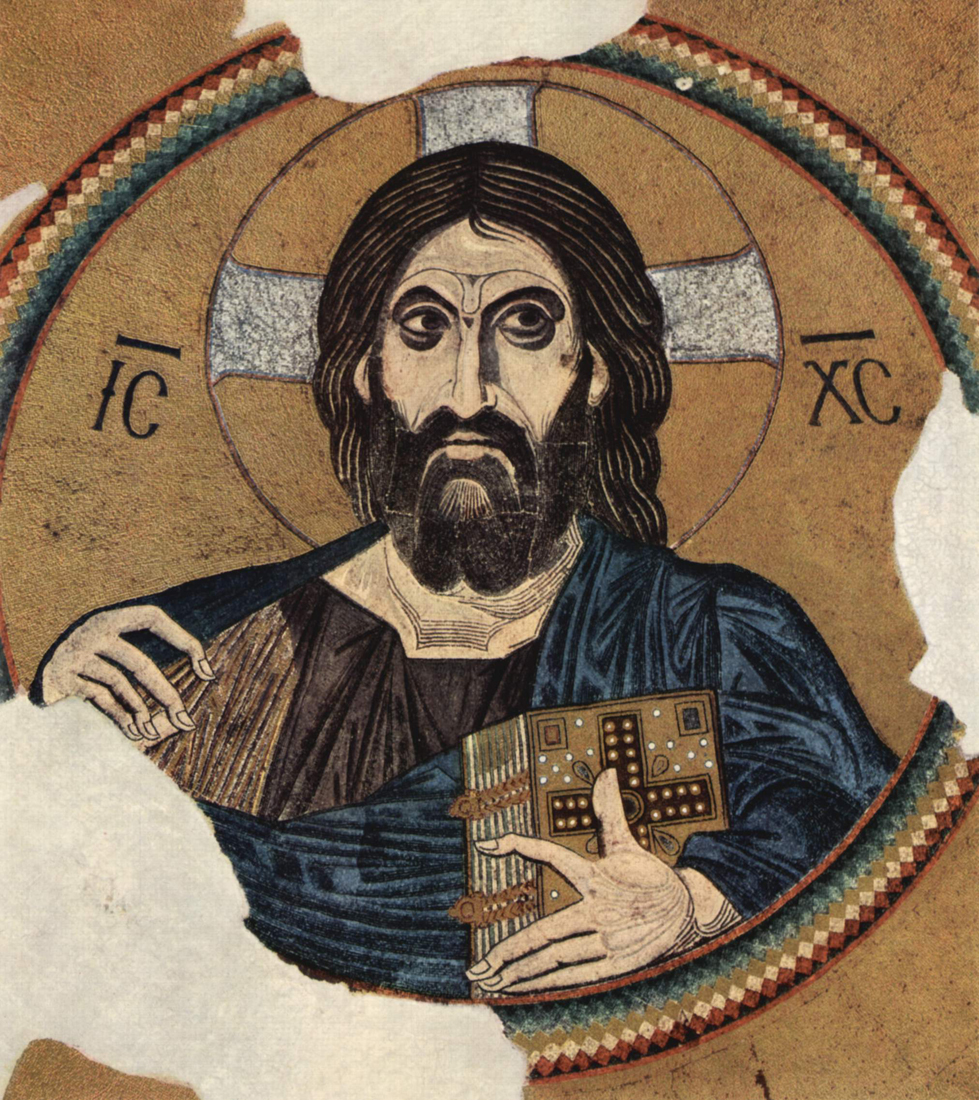




Byzantine Art And Architecture Art History Teaching Resources



Byzantium Ca 330 1453 Essay The Metropolitan Museum Of Art Heilbrunn Timeline Of Art History




Byzantine Art Artsy




Byzantine Mosaics 255 Artworks Mosaic



Byzantium Ca 330 1453 Essay The Metropolitan Museum Of Art Heilbrunn Timeline Of Art History




Early Byzantine Art Boundless Art History




Beginner S Guide To Byzantine Art Mosaics Article Khan Academy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿